Stress causes neutrophils to form sticky ‘web-like structures’, making body tissues more susceptible to cancer metastasis. The study published in Cancer Cell, 22 February, demonstrated that the stress hormone glucocorticoid leads to the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), known to drive metastasis-promoting microenvironments.
“What’s novel and exciting about our study is that we have discovered that stress hormones can trigger the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps,” Mikala Egeblad, the senior author, tells Cancerworld. “These stress-induced NETs in turn play a critical role in promoting metastasis by creating a favourable environment (or ‘niche’) in the lungs that helps the cancer cells that get to the lung grow more easily.”
Egeblad, who undertook the study while working at the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, says the discovery could have important therapeutic implications. “This new finding helps us better understand how stress can impact the spread of cancer and may provide new opportunities for treating and preventing metastasis.”
Cancer patients have many sources of severe stress, including worrying about their prognosis and enduring weeks of therapy. Chronic stress has been found to be associated with an increased risk of metastasis and poor survival in cancer patients. It is known to activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, resulting in the release of glucocorticoid stress hormones (cortisol in humans and corticosterone in mice). Furthermore, glucocorticoids bind to the glucocorticoid receptor to form a receptor-ligand complex, which regulates gene expression. An additional known factor is that an elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio indicates a dysregulated balance between innate and adaptive immune cells and has been associated with poor prognosis in breast and other cancers.
For the current study, the team used two mouse models to determine how chronic stress affects neutrophils to promote metastasis. In the first model, they exposed mice to the stressful situation of being limited to a very small space where they could not move freely. “This stimulates predictable stress that may resemble the chronic stress experienced after a cancer diagnosis,” explains Egeblad, who recently moved to John Hopkins University, Baltimore.
In the second model, they randomly exposed mice to 12 different milder stressors (e.g. short-term withholding of food or water or overnight exposure to light). “This model simulated the unpredictable stress experienced by cancer patients, such as worries about treatment responses or financial concerns.”
First, the team showed that both stress models increased corticosterone levels in mouse plasma.
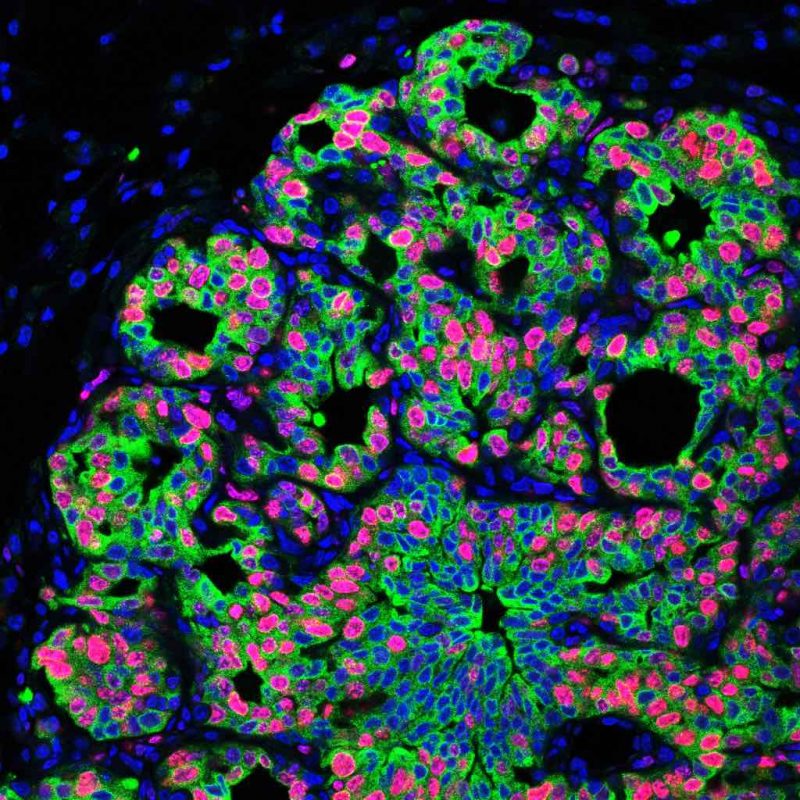
With the models, the team went on to demonstrate that exposing the mice to different types of chronic stress significantly increased metastasis, with mice subjected to chronic stress exhibiting two- to four-fold higher levels of metastasis to lung or spleen from disseminated cancer cells in comparison to non-stressed mice.
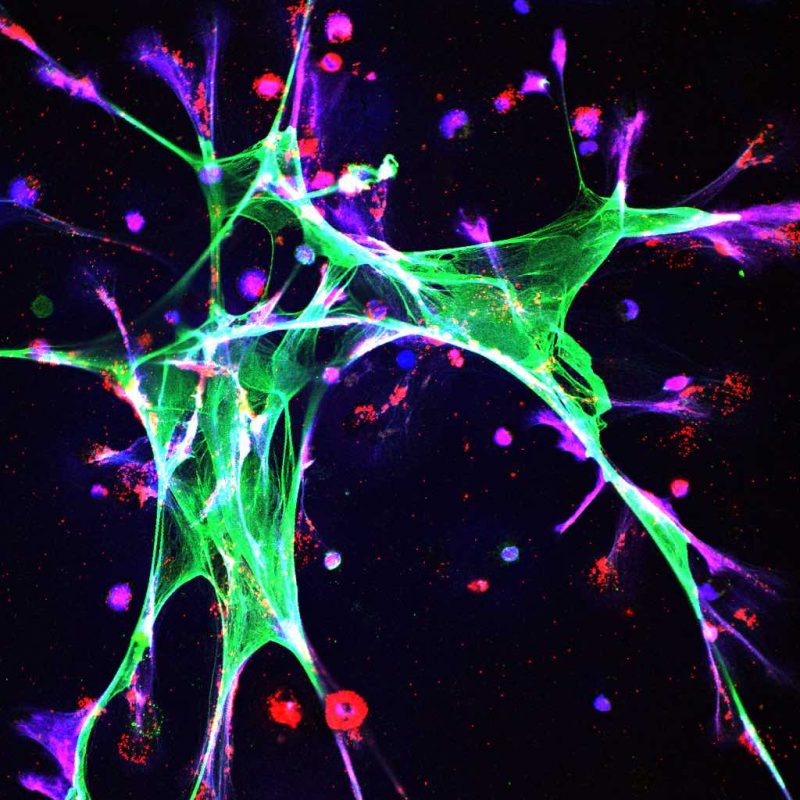
To characterise the microenvironmental changes, the team analysed the lungs of mice subjected to chronic stress with bulk RNA sequencing. Mice exposed to stress, they found, had more extracellular matrix (including fibronectin), fewer T cells, and more neutrophils.
Focusing attention on neutrophils, they showed that, if the number of neutrophils was depleted using antibodies, then mice exposed to stress no longer had increased metastasis.
They went on to show that stress induces neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation (DNA scaffolds formed as a defence to immobilise invading micro-organisms) through glucocorticoid receptor signalling. The key finding for this conclusion was that, if stressed mice were genetically engineered to have neutrophils that could not respond to glucocorticoids, then chronic stress no longer caused the formation of NETs, increased accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, or increased metastasis. If NETs were targeted with DNase I (an enzyme that breaks down DNA in NETs), again no increase in metastasis was found when mice were stressed.
“Our findings indicate that stress-induced changes to the host, such as neutrophil dysregulation and formation of NET’s, may contribute to the promotion of metastasis,” Egeblad tells Cancerworld.
It may therefore be beneficial, she adds, to integrate stress management into the routine care of cancer patients. “Developing strategies targeting neutrophils or NETs could prevent metastasis for patients where other stress-reducing interventions might be difficult,” says Egeblad.
In cell culture experiments the investigators showed inhibitors of CDK4/6, cathepsin G, and ROS all blocked glucocorticoid-induced NET formation. “Among these molecules, CDK4/6 inhibitors palbociclib and abemaciclib are already approved for cancer treatment,” says Egeblad.
Before initiating clinical trials looking at stress interventions and pharmaceutical treatments, studies will first be needed to validate the effects of stress on metastasis in patients.
One concerning issue arising from the study was the cancer promoting effects of glucocorticoids, given that synthetic glucocorticoids are commonly used to overcome the side effects of chemotherapy and treat symptoms in patients with advanced cancer. “We want to emphasise that clinical studies are needed to address whether synthetic glucocorticoids have potentially overlooked longer term risks. It is likely that the acute clinical benefits of synthetic glucocorticoids outweigh any potential negative long-term risks,” says Egeblad.