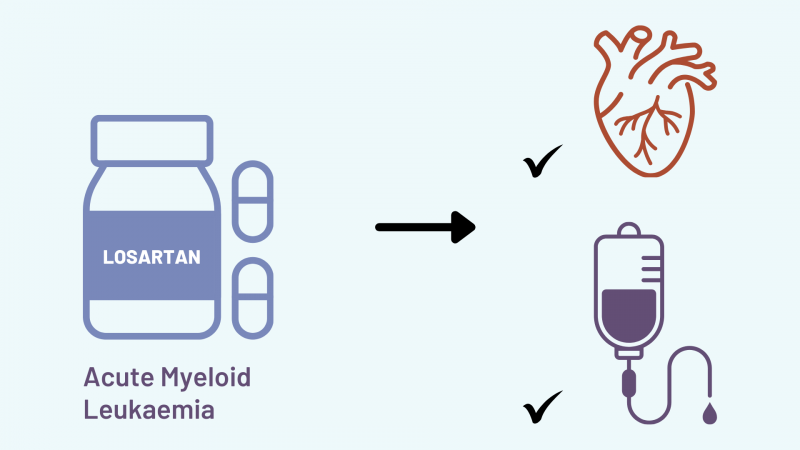
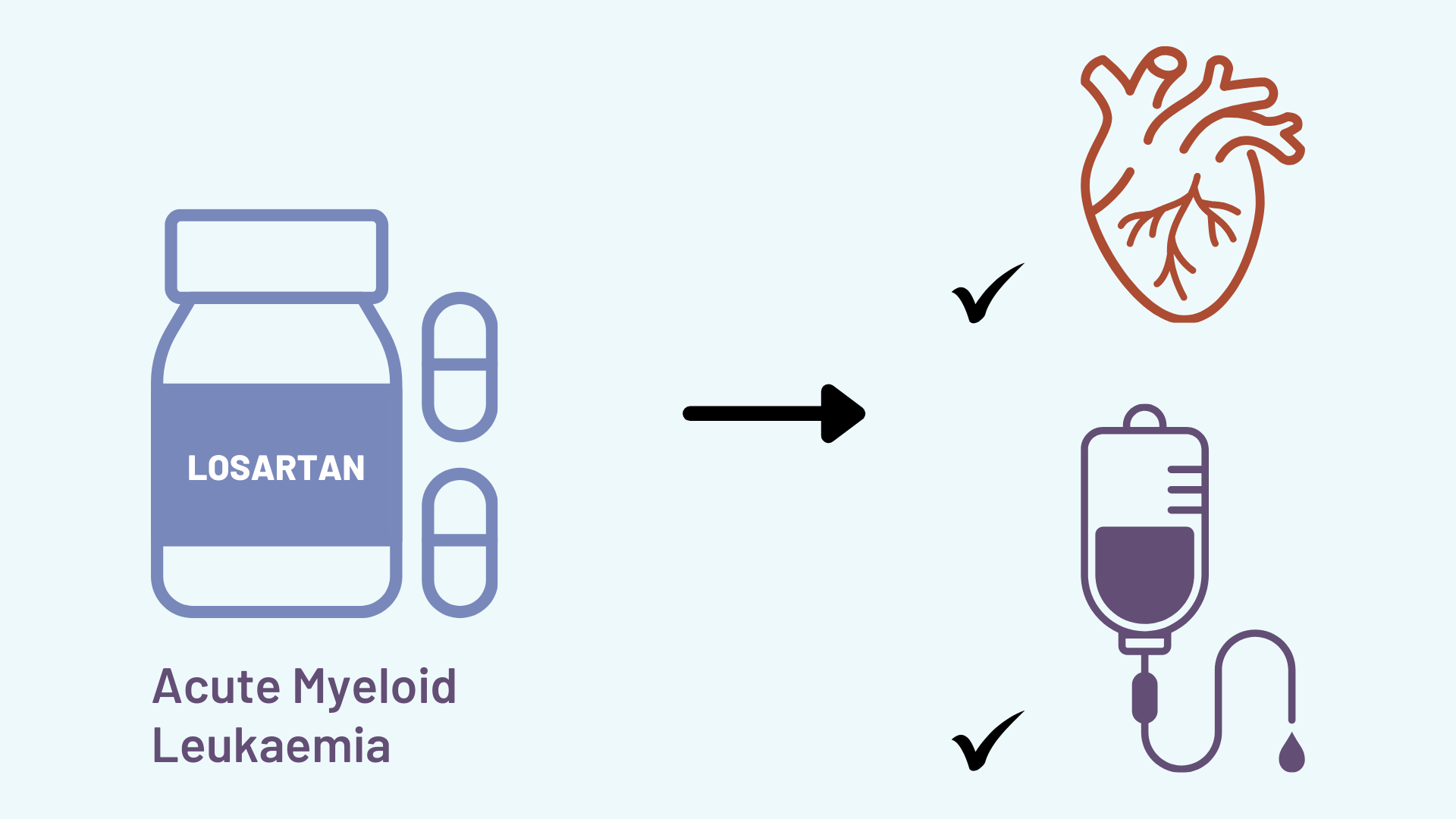
Treating acute myeloid leukaemia with losartan, a commonly used blood pressure agent, achieved the dual benefits of enhancing chemotherapy efficacy and preventing cardiotoxicity in a mouse model. The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, 19 June, demonstrated both benefits were achieved through blockade of the well-known cardiovascular disease target, angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AGTR1).
“When we treated mice with the AGTR1 inhibitor losartan, we observed that this clinically used drug shows great promise in reducing acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) development while protecting against chemotherapy induced cardiotoxicity,” says XunLei Kang, the corresponding author from the University of Missouri School of Medicine. “It also highlights the need for greater attention to be given to the cardiovascular health of patients undergoing chemotherapy.”
AML, a blood cancer affecting monocytes and granulocytes derived from myeloid stem cells, is typically treated with intensive chemotherapy, which can be limited by cardiotoxicity. Patients with AML, especially those receiving intensive chemotherapy, have a high incidence of cardiovascular disease events. “This close association suggests the potential for shared targets between AML and CVD [cardiovascular disease] that could be used to treat AML and protect cardiovascular function at the same time,” Kang tells Cancerworld.
The team first analysed whole-blood RNA sequences from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA ) for AML. Using uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP), an algorithm that reduces the complexity of human transcriptomics data and groups patients with similar gene expression patterns, the investigators identified nine shared genes that occurred between AML and cardiovascular disease. The genes ultimately led them to focus on AGTR1, the protein receptor best known for mediating the vasoconstrictor effects of angiotensin II. The team went on to hypothesise that inhibition – or ‘knockout’ – of AGTR1 might serve the dual function of suppressing AML while at the same time protecting against cardiotoxicity.
The researchers created a mouse model of AML by transducing AML oncogenes (such as MLL-AF9 and AML-ET09) into the haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of mice. They then used short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) to ‘knockdown’ AGTR1 in human AML cells. Combining multi-omics and biochemistry methods, they explored genetic changes after AGTR1 knockout, leading to identification of a pivotal role for the AGTR1-Notch1 axis. Reintroduction of the Notch1 cell surface receptor into AGTR1 ‘knockout’ mice reversed AML suppression, confirming Notch1 as the downstream effector of AGTR1.
To evaluate AGTR1 inhibition in a clinically relevant way, the team transplanted human AML cells into immunodeficient mice treated with chemotherapy and the AGTR1 inhibitor losartan. The results showed that losartan enhanced chemotherapy efficacy against AML by approximately 50% and improved left ventricular ejection fractions (a surrogate for reduced cardiotoxicity) by approximately 30%.
“We found that targeting AGTR1 suppressed AML development and protected cardiovascular function against cardiotoxicity induced by AML and chemotherapy. This is regulated by the AGTR1-Notch1 axis. In AML, Notch1 functions as a transcription factor and regulates a variety of genes associated with stemness and chemoresistance,” write the authors.
The team have filed a patent for their findings, and are actively seeking collaborators to perform a human clinical trial. If the findings are confirmed in clinical trials, says Kang, the approval process to use losartan could be faster compared to other medications, since it is already FDA-approved and will not require extensive new safety data.
The study, Kang adds, raises the possibility that losartan might be beneficial in other blood cancers and solid tumours. In chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML), for example, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are known to cause cardiotoxicity. Furthermore, prior studies have shown that losartan can suppress progression of solid tumours, including liver and breast cancer. “We believe losartan could also help prevent cardiotoxicity and enhance chemotherapy in other solid tumours and blood cancers,” says Kang.