News
Cancer survivors who are less lonely live longer
Greater feelings of loneliness are associated with higher mortality rates among cancer survivors. The study, published in the Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (JNCCN), April 25, found that cancer patients reporting severe loneliness had a 67% higher all-cause…
Plant-based diets lower risk of progression in prostate cancer
Higher intakes of plant foods following a diagnosis of prostate cancer were associated with lower risks of cancer progression. The study, published in JAMA Netw Open, 1 May, found men diagnosed with early prostate cancer whose plant food intake was…
Extracellular vesicles from injured hearts accelerate tumour growth
Small extracellular vesicles secreted by the hearts of mice with myocardial infarction accelerated the growth of lung cancer tumours already present in the same mice. The study, published online in Circulation, 15 March, found that the cardiovascular drug spironolactone reduced…
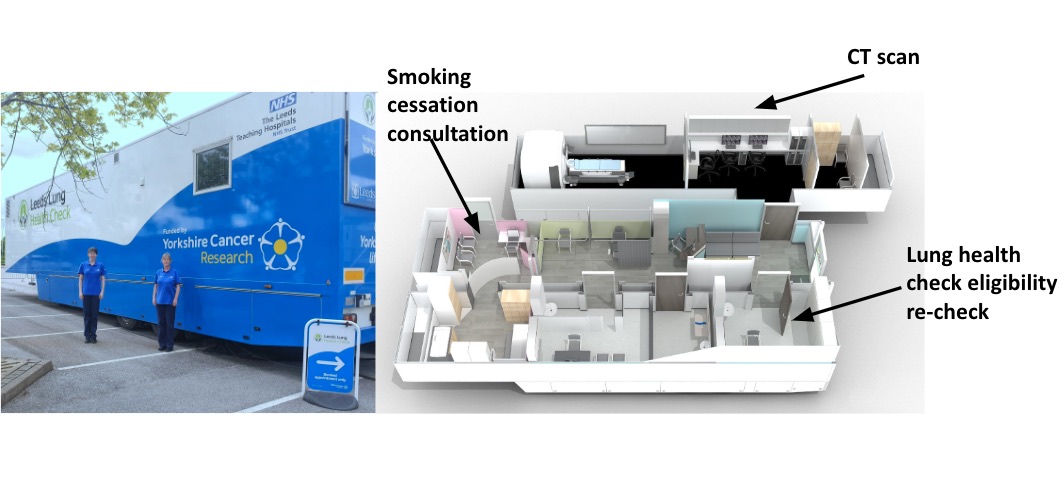
One-stop lung screening and smoking cessation advice works
Offering ‘stop smoking’ support as part of a national lung cancer screening programme resulted in nearly nine out of ten people agreeing to an immediate consultation and three-quarters accepting longer term support. The evaluation of an ‘opt-out’ face-to-face smoking cessation…
New drug combination offers potential to prevent bone metastasis
A combination of existing drugs may inhibit development of bone metastasis in breast cancer patients. The study published in Cancer Discovery, 1 March, found that a combined treatment strategy that activates T cells while at the same time targeting cells…
Slowing ‘accelerated ageing’ may offer new avenue for cancer prevention
Accelerated ageing is more common in recent birth cohorts and associated with increased incidence of early-onset solid tumours. The study, abstract 846, presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting, held April 5–10, in San Diego, found…
Secondhand smoke reduces cisplatin impact on head & neck tumour cells
Secondhand smoke significantly reduced the ability of chemotherapy to kill head and neck cancer cells and increased the cells’ ability to reproduce. The study, published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, found that secondhand smoke altered the proteins that…
EBCC manifesto urges action to overcome disparities in metastatic breast cancer
All patients with metastatic breast cancer should have equal access to the best treatments and outcomes regardless of where they live in Europe. The EBCC14 manifesto, agreed at the 14th European Breast Cancer Conference (EBCC) on March 22 in Milan,…
Cancer Grand Challenge projects to shine light on unanswered oncology questions
The Cancer Grand Challenges initiative has announced the five global research teams who between them will receive $125 million to address unanswered questions. The winning teams, revealed in March, are addressing four major oncology challenges – solid tumours in children,…
Childhood cancer survivors need younger monitoring for cardiovascular disease
Survivors of childhood cancer are at a significantly higher risk of death following a major cardiovascular event than the general public. The study, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology 27 February, found risk of death after…